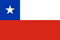
The most common pathology of the genitourinary system in men is inflammatory disease of the prostate gland. According to statistics, prostatitis is diagnosed in every 10 patients in adulthood. Without adequate treatment, the disease progresses rapidly, leads to serious complications and affects a man's sex life.
Symptoms of the disease
Any disease is easier to treat when diagnosed at an early stage. Prostatitis occurs in both acute and complicated forms - chronic, which occurs with neglected inflammation of the prostate. The symptoms and treatment of the disease vary and depend on its stage and type. In the acute course of the pathology a person experiences:

- Difficulty urinating. One of the first signs is problems with the passage of urine due to narrowing of the ureter. In the early stages, the prostate begins to grow and slightly compresses the ducts.
- Pain in the lower abdomen, which is most often disturbed after exercise or at the end of the day. The pain of sensation and intensity are different: they can be pulling, cutting, aching. They then spread through the scrotum and penis and are inserted into the rectum during defecation. The disease provokes constipation, which only exacerbates the inflammatory process in the prostate gland.
- Frequent urination. A man who has not previously woken up to empty his bladder can go to the toilet 1-2 times a night at the beginning of the disease. With the transition of prostatitis to another form, the desire to urinate decreases. It gives the impression of overcrowding of the bladder, and after going to the toilet - incomplete emptying.
- Visual change in urine. Impurities of pus or blood can be found in the urine in the early stages of the pathology.
- The emergence of sexual dysfunction. Men experience erection problems and severe pain during ejaculation.
- Prolonged increase in body temperature in the region of 39 degrees, which is accompanied by chills, weakness and body aches.
Most of the symptoms of the disease are pronounced. The task of men is to carefully monitor the condition of their body and its changes, not to miss the first signs and not to allow the pathology to develop into a chronic stage.
The first manifestations of inflammation of the prostate gland in the stronger sex in a neglected form are almost the same as in the acute phase of the disease. But they are accompanied by symptoms such as:

- Decreased libido, loss of erection during intercourse, detection of blood in semen.
- Frequent urge to urinate, fullness in the bladder, white scales in the urine. During exacerbations, the man may be completely deprived of the ability to empty the bladder, as an inflamed prostate blocks the passage of urine into the urethra.
- Depression, insomnia or drowsiness. Men suffering from diseases such as prostatitis often experience bouts of anger or aggression associated with psycho-emotional disorder.
To avoid mistakes in making the correct diagnosis, it makes sense to be examined by several doctors and in different institutions. Symptoms and treatment of prostatitis, like any other disease of the genitourinary system, is not a problem that should be postponed or saved for health.
Reasons for development
It is almost impossible to determine the root cause of the pathology. At the same time, there are not so few provoking factors, each of them is very serious, especially given the male habit of neglecting health. Main reasons:

- The formation of congestion in the pelvic area. They are characterized by slow blood circulation, in which tissue nutrition deteriorates, edema occurs and capillary function is impaired.
- Hypothermia. By freezing even once, men themselves provoke the development of inflammation of the prostate gland.
- Sedentary lifestyle in which the stronger sex sit for hours in one position. No less harmful factor is the work associated with vibrations (tractor drivers). With constant shaking, the perineum is injured and the organs in the pelvic area are weakened, which creates additional conditions for inflammation.
- Transmitted venereal diseases. Sexually transmitted infections cannot bypass the prostate. Even after treatment, immunity decreases and the prostate gland becomes vulnerable.
- Stool retention. Constipation creates increased stress when emptying the rectum, injuring the prostate. In addition, stagnation is intensified and toxins are reabsorbed, including in the closely spaced prostate gland.
- Extremes in intimate life. Deficiency and excess of sex also negatively affect reproductive health. With excessive activity, the prostate wears out, and abstinence increases stagnation in it.
- Interruption of sexual intercourse. As a method of contraception, it is recognized as ineffective and undermines men's health. Attempts to control a physiological process that is already underway are very harmful.
- Alcohol abuse, malnutrition. These two factors lead to swelling of the prostate and the appearance of malignant neoplasms.
- Urological diseases. Due to the close anatomical connection with the reproductive system, inflammatory processes in the urinary system can penetrate a little lower and affect the prostate.
By identifying the causes that contributed to the development of inflammation, the urologist individually chooses the treatment, while excluding adverse factors.
Methods of treatment
Treatment of prostatitis should be comprehensive. After diagnosing the disease, the doctor, as a rule, prescribes an individual treatment regimen. The patient needs at least 4-6 months to achieve a positive effect. Today, many different methods of treatment are used, including drug therapy, the use of physiotherapy procedures and massage. In official medicine, these methods are recognized as the most effective and safe for the health of the stronger sex.

Qualified psychotherapy is considered to be an equally important measure, as the constant painful sensations and problems that have arisen in the intimate life have a negative impact not only on the general well-being of the patient, but also on his psychological state.
Medical therapy
Surgical treatment is indicated in cases where medical measures have failed or the prostate gland blocks the flow of urine. Surgery can lead to infertility, so it is not prescribed to young men.

In infectious prostatitis, antibacterial therapy is performed. When the cause of the pathology is not bacteria or viruses, antibiotic treatment is considered pointless. Alpha-blockers are used to relax the muscles of the prostate, improve urine flow and relieve pain in the perineal area.
Muscle relaxants will help reduce pain and relieve muscle tension in the pelvic area. Severely ill patients are prescribed droppers with diuretics, which contribute to the abundant excretion of urine and prevent further intoxication of the body.
The course of treatment should be completed, even if the symptoms of the disease have completely disappeared. Signs of prostatitis often disappear at the very beginning of antibiotic therapy, but become chronic when treatment is stopped.
Nonbacterial prostatitis requires a different treatment regimen. It consists of taking analgesics and antipyretics.
Simultaneously with the main treatment, the urologist prescribes maintenance therapy, which includes bed rest, drinking plenty of water and sitting baths. Patients should follow a diet that limits alcohol, caffeine, fatty and spicy foods.
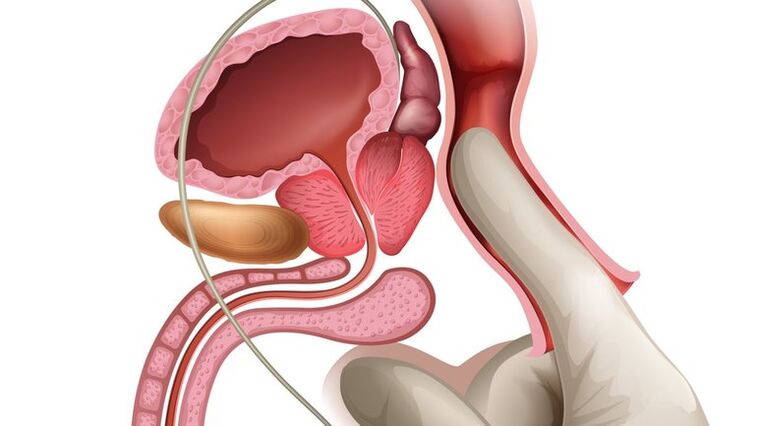
In chronic inflammation of the prostate gland, the most effective remedy is regular prostate massage, which reduces the likelihood of re-inflammation. The course of treatment consists of 10 sessions. Contraindications to the procedures are rectal cancer and exacerbation of prostatitis.
Physiotherapy is used not only as a treatment, but also for prevention. Improves blood circulation, increases muscle tone, accelerates tissue regeneration and increases cell permeability. It is forbidden to use this method in high blood pressure, fever, epilepsy, cancer, urolithiasis, anemia, kidney disease and cardiovascular disease.
The use of rectal suppositories reduces the negative impact on the functioning of internal organs. Suppositories may contain antibiotics, herbs, antispasmodics. They eliminate swelling, relieve inflammation and restore urination.
Folk ways
The therapy of pathology at home with the help of recipes for alternative medicine is effective only at an early stage. There are many ways to eliminate the main symptoms of inflammation:
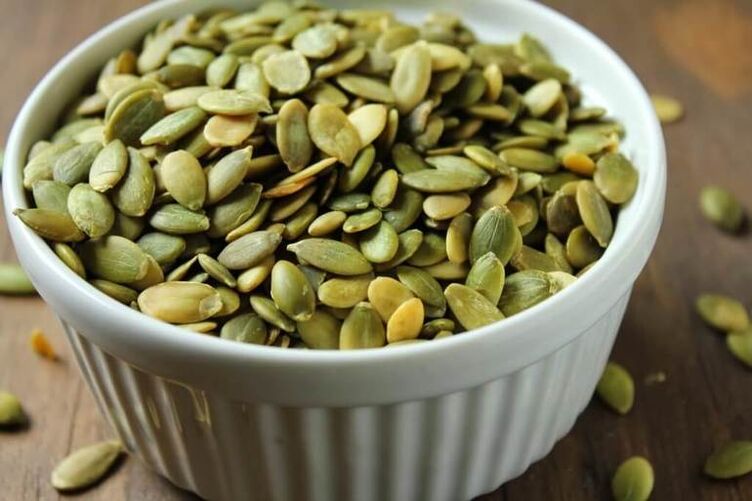


- The fried pumpkin seeds (500 g) are twisted in a meat grinder, then honey (200 g) is added and mixed well. Pumpkin-honey mixture is used to make balls no bigger than a walnut. Dissolve half an hour before each meal, 1 piece for 2-3 minutes. The product is stored in the refrigerator. Pumpkin seeds contain a large amount of zinc, which is necessary to maintain the normal functioning of the genitourinary system.
- The crushed and dried aspen bark (100 g) is placed in a half-liter jar and poured with vodka (200 g). The container is tightly closed, left to infuse in a dark place. After two weeks, the tincture is filtered and consumed 20 drops, diluted in a quarter cup of water, 3 times daily before meals.
- Honey (1 tsp. ), Egg (1 tsp. ) Are mixed with rye flour (3 tbsp. ), From the dough are made thin suppositories, the diameter of which should be no more than 1 cm. Store in the refrigerator. In the morning and evening they are inserted into the anus after emptying the rectum. The course of treatment is about 4 weeks, after which a break is made and the therapy is repeated.
- The small onion (3 pieces) is rubbed on a fine grater, poured with boiling water (3 tablespoons) and insist for one day. The decoction is taken 50 ml every hour.
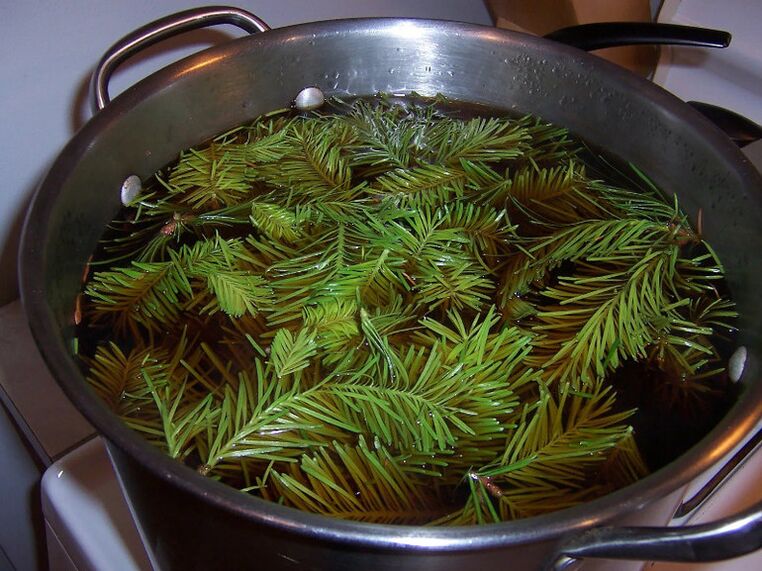
- Pine branches (200 g) together with boiled water (2 l) are stewed on low heat for 2-3 hours. Once the decoction boils, it turns into an extract. Prepare such a concentrate just before taking a warm bath. The water level should not be higher than the middle of the chest. The pelvic area is rubbed with the drug for 15 minutes until redness appears. The therapy is carried out daily for 2 weeks. Baths have an antimicrobial effect, relieve pain and improve urination.
As good as the effect of folk remedies is, it is difficult for them to compete with the achievements of pharmacology. The most correct and effective solution will be an integrated approach to the treatment of prostatitis.